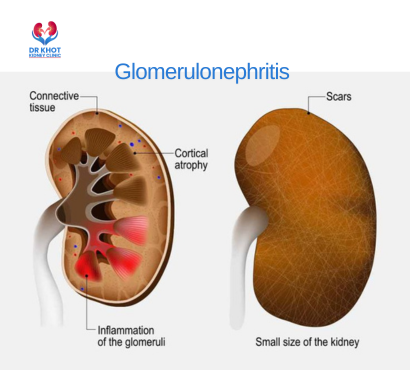
Glomerulonephritis (GN) is a group of kidney diseases characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli—the tiny blood-filtering units in the kidneys. This inflammation can reduce kidney function and lead to serious complications like chronic kidney disease or kidney failure if untreated. Early recognition, diagnosis, and treatment are crucial to preserving kidney health. This blog explains types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of glomerulonephritis with relevance to Indian healthcare contexts.
What Is Glomerulonephritis?
- Inflammation damages the filtering membranes in kidneys, impairing the removal of waste and excess fluids from the body.
- GN may be acute (rapid onset) or chronic (progressing slowly over years).
- It may occur as a primary disease or secondary to systemic conditions like lupus or infections.
Causes
- Immune responses to infections (post-strep throat)
- Autoimmune diseases causing direct attack on glomeruli
- Genetic conditions (e.g., Alport syndrome)
- Exposure to toxins or drugs
- Diabetes and hypertension as secondary contributors
Symptoms
- Swelling (edema) in face, hands, feet
- Blood in urine (visible or microscopic)
- Proteinuria (foamy urine)
- High blood pressure
- Fatigue and decreased urine output in advanced stages
Diagnosis
- Urinalysis with protein and blood tests
- Blood tests for kidney function (creatinine, BUN)
- Imaging such as ultrasound if structural evaluation needed
- Kidney biopsy for definitive diagnosis and type classification
Treatment
- Address underlying cause (infection, autoimmune disease)
- Immunosuppressive medications like corticosteroids for autoimmune GN
- Blood pressure control with ACE inhibitors/ARBs
- Dietary modifications: low salt, protein control, fluid management
- Dialysis or transplant in end-stage renal disease
Prognosis and Indian Context
- Early treatment improves outcomes.
- Lack of awareness and late presentation is common in India.
- Availability of nephrology specialists varies; telemedicine and public health initiatives help improve care.
FAQ
- Can glomerulonephritis be cured?
Acute cases may resolve fully with treatment but chronic GN requires ongoing management to delay progression. - Is GN contagious?
No, but some infections triggering GN can spread. - How to prevent kidney damage with GN?
Early diagnosis, medication adherence, blood pressure control, and lifestyle changes are key.